Under Which Step Of The Design Process Are Computer Generated Drawings Created?
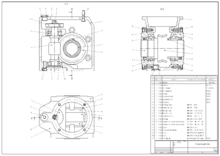
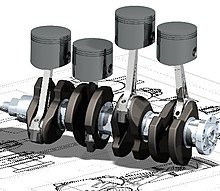
Figurer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or workstations ) to assistance in the cosmos, modification, analysis, or optimization of a blueprint.[1] This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, meliorate communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing.[2] Designs made through CAD software are helpful in protecting products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the grade of electronic files for impress, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms estimator-aided drafting (CAD) and computer aided design and drafting (CADD) is as well used.[three]
Its use in designing electronic systems is known as electronic design automation (EDA). In mechanical design information technology is known equally mechanical design automation (MDA), which includes the process of creating a technical cartoon with the employ of computer software.[iv]
CAD software for mechanical blueprint uses either vector-based graphics to depict the objects of traditional drafting, or may also produce raster graphics showing the overall appearance of designed objects. However, it involves more than just shapes. Every bit in the manual drafting of technical and technology drawings, the output of CAD must convey information, such equally materials, processes, dimensions, and tolerances, according to application-specific conventions.
CAD may exist used to design curves and figures in 2-dimensional (2D) infinite; or curves, surfaces, and solids in three-dimensional (3D) space.[5] [six] : 71, 106
CAD is an of import industrial art extensively used in many applications, including automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, industrial and architectural design, prosthetics, and many more than. CAD is likewise widely used to produce computer animation for special effects in movies, advertising and technical manuals, ofttimes chosen DCC digital content creation. The modern ubiquity and power of computers ways that even perfume bottles and shampoo dispensers are designed using techniques unheard of by engineers of the 1960s. Because of its enormous economical importance, CAD has been a major driving force for research in computational geometry, computer graphics (both hardware and software), and discrete differential geometry.[seven]
The design of geometric models for object shapes, in detail, is occasionally called reckoner-aided geometric blueprint (CAGD).[eight]
Uses [edit]
Computer-aided blueprint is 1 of the many tools used by engineers and designers and is used in many means depending on the profession of the user and the type of software in question.
CAD is one function of the whole digital product development (DPD) action within the product lifecycle management (PLM) processes, and as such is used together with other tools, which are either integrated modules or stand-alone products, such as:
- Computer-aided engineering (CAE) and finite chemical element analysis (FEA, FEM)
- Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) including instructions to computer numerical control (CNC) machines
- Photorealistic rendering and motion simulation.
- Document management and revision command using production data management (PDM)
CAD is besides used for the accurate creation of photo simulations that are frequently required in the grooming of environmental bear upon reports, in which figurer-aided designs of intended buildings are superimposed into photographs of existing environments to represent what that locale will be like, where the proposed facilities are allowed to be built. Potential blockage of view corridors and shadow studies are also frequently analyzed through the utilize of CAD.[9]
CAD has been proven to be useful to engineers likewise. Using four properties which are history, features, parameterization, and high-level constraints. The construction history can exist used to expect dorsum into the model'south personal features and work on the single surface area rather than the whole model. Parameters and constraints tin can be used to decide the size, shape, and other backdrop of the different modeling elements. The features in the CAD system can be used for the variety of tools for measurement such as tensile forcefulness, yield force, electrical, or electromagnetic backdrop. Also its stress, strain, timing, or how the element gets afflicted in certain temperatures, etc.
Types [edit]

A elementary procedure of recreating a solid model out of 2D sketches.
At that place are several unlike types of CAD,[10] each requiring the operator to think differently about how to utilise them and pattern their virtual components in a dissimilar way for each.
There are many producers of the lower-end 2nd systems, including a number of free and open-source programs. These provide an approach to the cartoon process without all the fuss over scale and placement on the drawing canvass that accompanied hand drafting since these tin exist adapted as required during the creation of the final draft.
3D wireframe is basically an extension of 2D drafting (not often used today). Each line has to exist manually inserted into the cartoon. The final product has no mass properties associated with information technology and cannot have features directly add to it, such as holes. The operator approaches these in a similar fashion to the 2d systems, although many 3D systems allow using the wireframe model to brand the final engineering drawing views.
3D "dumb" solids are created in a fashion coordinating to manipulations of real-world objects (not often used today). Basic three-dimensional geometric forms (prisms, cylinders, spheres, rectangle) have solid volumes added or subtracted from them every bit if assembling or cut real-world objects. 2-dimensional projected views can easily exist generated from the models. Basic 3D solids don't usually include tools to easily allow the motion of the components, fix their limits to their motion, or place interference between components.
There are two types of 3D solid modeling
- Parametric modeling allows the operator to utilize what is referred to as "blueprint intent". The objects and features are created modifiable. Any future modifications tin can be made by irresolute on how the original office was created. If a feature was intended to be located from the middle of the part, the operator should locate it from the center of the model. The feature could be located using any geometric object already bachelor in the part, simply this random placement would defeat the design intent. If the operator designs the part as it functions the parametric modeler is able to make changes to the part while maintaining geometric and functional relationships.
- Direct or explicit modeling provide the power to edit geometry without a history tree With straight modeling, once a sketch is used to create geometry the sketch is incorporated into the new geometry and the designer just modifies the geometry without needing the original sketch. As with parametric modeling, direct modeling has the power to include the relationships between selected geometry (e.thousand., tangency, concentricity).
The top-end systems offer the capabilities to contain more organic, artful and ergonomic features into the designs. Freeform surface modeling is oftentimes combined with solids to allow the designer to create products that fit the homo course and visual requirements every bit well as they interface with the automobile.
Technology [edit]

Originally software for CAD systems was developed with reckoner languages such as Fortran, ALGOL simply with the advancement of object-oriented programming methods this has radically changed. Typical mod parametric feature-based modeler and freeform surface systems are built effectually a number of key C modules with their ain APIs. A CAD system tin be seen as congenital upwards from the interaction of a graphical user interface (GUI) with NURBS geometry or purlieus representation (B-rep) information via a geometric modeling kernel. A geometry constraint engine may also be employed to manage the associative relationships between geometry, such as wireframe geometry in a sketch or components in an assembly.
Unexpected capabilities of these associative relationships have led to a new form of prototyping chosen digital prototyping. In contrast to physical prototypes, which entail manufacturing fourth dimension in the pattern. That said, CAD models can be generated past a computer after the physical prototype has been scanned using an industrial CT scanning machine. Depending on the nature of the business, digital or physical prototypes can exist initially chosen co-ordinate to specific needs.
Today, CAD systems exist for all the major platforms (Windows, Linux, UNIX and Mac OS X); some packages support multiple platforms.[11]
Currently, no special hardware is required for most CAD software. Even so, some CAD systems can do graphically and computationally intensive tasks, so a modern graphics card, high speed (and perhaps multiple) CPUs and large amounts of RAM may be recommended.
The human being-machine interface is generally via a computer mouse but can likewise exist via a pen and digitizing graphics tablet. Manipulation of the view of the model on the screen is also sometimes washed with the use of a Spacemouse/SpaceBall. Some systems also support stereoscopic glasses for viewing the 3D model. Technologies which in the past were express to larger installations or specialist applications take go bachelor to a wide grouping of users. These include the CAVE or HMDs and interactive devices like motion-sensing technology
Software [edit]
Starting around the mid-1960s, with the IBM Drafting System, computer-aided design systems began to provide more adequacy than just an power to reproduce manual drafting with electronic drafting, the cost-do good for companies to switch to CAD became apparent. The benefits of CAD systems over manual drafting are the capabilities one often takes for granted from computer systems today; automated generation of bills of materials, auto layout in integrated circuits, interference checking, and many others. Eventually, CAD provided the designer with the ability to perform engineering calculations.[vi] During this transition, calculations were still performed either by hand or by those individuals who could run computer programs. CAD was a revolutionary change in the engineering industry, where draftsmen, designers, and engineering roles begin to merge. It did non eliminate departments as much as it merged departments and empowered draftsmen, designers, and engineers. CAD is an example of the pervasive effect computers were outset to have on the industry. Electric current computer-aided design software packages range from 2D vector-based drafting systems to 3D solid and surface modelers. Modern CAD packages tin can also frequently allow rotations in three dimensions, allowing viewing of a designed object from any desired angle, even from the inside looking out.[6] Some CAD software is capable of dynamic mathematical modeling.[6]
CAD technology is used in the design of tools and mechanism and in the drafting and design of all types of buildings, from small residential types (houses) to the largest commercial and industrial structures (hospitals and factories).[12]
CAD is mainly used for detailed engineering of 3D models or 2D drawings of concrete components, merely information technology is also used throughout the engineering process from conceptual blueprint and layout of products, through strength and dynamic analysis of assemblies to definition of manufacturing methods of components. It can also be used to design objects such as jewelry, piece of furniture, appliances, etc. Furthermore, many CAD applications now offering avant-garde rendering and blitheness capabilities so engineers can improve visualize their product designs. 4D BIM is a type of virtual structure engineering simulation incorporating time or schedule-related information for project direction.
CAD has get an specially of import technology within the telescopic of computer-aided technologies, with benefits such every bit lower product development costs and a greatly shortened design wheel. CAD enables designers to layout and develop piece of work on screen, print it out and save it for future editing, saving time on their drawings.
License management software [edit]
In the beginning of 2000, some CAD system software vendors might have shipped their distributions with a dedicated license manager software that might command how often or how many users can utilize CAD organization.[6] : 166 Information technology could run either on a local automobile (past loading from a local storage device) or a local network fileserver and was usually tied to a specific IP address in latter case.[6] : 166
List of software packages [edit]
CAD software enables engineers and architects to design, inspect and manage engineering projects inside an integrated graphical user interface (GUI) on a personal figurer organization. Almost applications support solid modeling with boundary representation (B-Rep) and NURBS geometry, and enable the same to be published in a variety of formats. A geometric modeling kernel is a software component that provides solid modeling and surface modeling features to CAD applications.
Based on market statistics, commercial software from Autodesk, Dassault Systems, Siemens PLM Software, and PTC dominate the CAD industry.[xiii] [14] The following is a list of major CAD applications, grouped by usage statistics.[15]
See also [edit]
- 3D figurer graphics
- 3D printing
- Additive Manufacturing File Format
- Algorithmic fine art
- CAD standards
- Coarse infinite (numerical analysis)
- Comparison of 3D reckoner graphics software
- Comparison of CAD, CAM, and CAE file viewers
- Comparison of figurer-aided design software
- Comparison of EDA software (Electronic Blueprint Automation)
- Estimator-aided industrial design
- Digital compages
- Electronic pattern automation
- Engineering science optimization
- Finite element method
- ISO 128
- ISO 10303 (Pace)
- Model-based definition
- Molecular design software
- Open-source hardware
- Rapid prototyping
- Responsive computer-aided pattern
- Space mapping
- Surrogate model
- System integration
- Virtual prototyping
- Virtual reality
References [edit]
- ^ Narayan, K. Lalit (2008). Computer Aided Blueprint and Manufacturing. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of Republic of india. p. iii. ISBN978-8120333420.
- ^ Narayan, K. Lalit (2008). Computer Aided Design and Manufacturing. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India. p. 4. ISBN978-8120333420.
- ^ Duggal, Vijay (2000). Cadd Primer: A General Guide to Computer Aided Design and Drafting-Cadd, CAD. Mailmax Pub. ISBN978-0962916595.
- ^ Madsen, David A. (2012). Engineering Drawing & Blueprint. Clifton Park, NY: Delmar. p. 10. ISBN978-1111309572.
- ^ Farin, Gerald; Hoschek, Josef; Kim, Myung-Soo (2002). Handbook of reckoner aided geometric design [electronic resources]. Elsevier. ISBN978-0-444-51104-1.
- ^ a b c d due east f Schoonmaker, Stephen J. (2003). The CAD guidebook : a basic transmission for understanding and improving estimator-aided design. New York: Marcel Dekker. ISBN0-8247-0871-7. OCLC 50868192.
- ^ Pottmann, H.; Brell-Cokcan, Southward. and Wallner, J. (2007) "Detached surfaces for architectural design" Archived 2009-08-12 at the Wayback Motorcar, pp. 213–234 in Bend and Surface Design, Patrick Chenin, Tom Lyche and Larry L. Schumaker (eds.), Nashboro Press, ISBN 978-0-9728482-7-v.
- ^ Farin, Gerald (2002) Curves and Surfaces for CAGD: A Practical Guide, Morgan-Kaufmann, ISBN ane-55860-737-iv.
- ^ "Computer-Aided Blueprint (CAD) and Estimator-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)". Inc.com . Retrieved 2020-04-30 .
- ^ "3D Feature-based, Parametric Solid Modeling". engineershandbook.com. Archived from the original on 2012-11-18. Retrieved 2012-03-01 .
- ^ "What is a CAD Workstation? Definition, Uses and More". Computer Tech Reviews. 2019-11-21. Retrieved 2020-04-30 .
- ^ Jennifer Herron (2010). "3D Model-Based Design: Setting the Definitions Straight". MCADCafe.
- ^ The Big 6 in CAD/CAE/PLM software manufacture (2011), CAEWatch, September 12, 2011
- ^ van Kooten, Michel (2011-08-23). "GLOBAL SOFTWARE TOP 100 – EDITION 2011". Software Top 100.
- ^ List of mechanical CAD softwares, BeyondMech
External links [edit]
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-aided_design
Posted by: woodardaffeekly.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Under Which Step Of The Design Process Are Computer Generated Drawings Created?"
Post a Comment