How To Create Text Columns In Illustrator
- Illustrator User Guide
- Get to know Illustrator
- Introduction to Illustrator
- What's new in Illustrator
- Common questions
- Illustrator system requirements
- Illustrator for Apple silicon
- Workspace
- Workspace basics
- Create documents
- Tools Default keyboard shortcuts | Illustrator
- Customize keyboard shortcuts
- Artboards
- Customize the workspace
- Properties panel
- Set preferences
- Touch Workspace
- Microsoft Surface Dial support in Illustrator
- Recovery, undo, and automation
- Rotate view
- Rulers, grids, and guides
- Accessibility in Illustrator
- Safe Mode
- View artwork
- Use the Touch Bar with Illustrator
- Files and templates
- Synchronize settings using Adobe Creative Cloud
- Introduction to Illustrator
- Illustrator on the iPad
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Illustrator on the iPad overview
- Illustrator on the iPad FAQs
- System requirements | Illustrator on the iPad
- What you can or cannot do on Illustrator on the iPad
- Workspace
- Illustrator on the iPad workspace
- Touch shortcuts and gestures
- Keyboard shortcuts for Illustrator on the iPad
- Manage your app settings
- Documents
- Work with documents in Illustrator on the iPad
- Import Photoshop and Fresco documents
- Select and arrange objects
- Create repeat objects
- Blend objects
- Drawing
- Draw and edit paths
- Draw and edit shapes
- Type
- Work with type and fonts
- Create text designs along a path
- Add your own fonts
- Work with images
- Vectorize raster images
- Color
- Apply colors and gradients
- Introduction to Illustrator on the iPad
- Cloud documents
- Basics
- Work with Illustrator cloud documents
- Share and collaborate on Illustrator cloud documents
- Upgrade cloud storage for Adobe Illustrator
- Illustrator cloud documents | Common questions
- Troubleshooting
- Troubleshoot create or save issues for Illustrator cloud documents
- Troubleshoot Illustrator cloud documents issues
- Basics
- Add and edit content
- Drawing
- Drawing basics
- Edit paths
- Draw pixel-perfect art
- Draw with the Pen, Curvature, or Pencil tool
- Draw simple lines and shapes
- Image Trace
- Simplify a path
- Define perspective grids
- Symbolism tools and symbol sets
- Adjust path segments
- Design a flower in 5 easy steps
- Perspective drawing
- Symbols
- Draw pixel-aligned paths for web workflows
- 3D effects and Adobe Substance materials
- About 3D effects in Illustrator
- Create 3D graphics
- Create 3D objects
- Create 3D Text
- About 3D effects in Illustrator
- Color
- About color
- Select colors
- Use and create swatches
- Adjust colors
- Use the Adobe Color Themes panel
- Color groups (harmonies)
- Color Themes panel
- Recolor your artwork
- Painting
- About painting
- Paint with fills and strokes
- Live Paint groups
- Gradients
- Brushes
- Transparency and blending modes
- Apply stroke on an object
- Create and edit patterns
- Meshes
- Patterns
- Select and arrange objects
- Select objects
- Layers
- Group and expand objects
- Move, align, and distribute objects
- Stack objects
- Lock, hide, and delete objects
- Duplicate objects
- Rotate and reflect objects
- Reshape objects
- Crop images
- Transform objects
- Combine objects
- Cut, divide, and trim objects
- Puppet Warp
- Scale, shear, and distort objects
- Blend objects
- Reshape using envelopes
- Reshape objects with effects
- Build new shapes with Shaper and Shape Builder tools
- Work with Live Corners
- Enhanced reshape workflows with touch support
- Edit clipping masks
- Live shapes
- Create shapes using the Shape Builder tool
- Global editing
- Type
- Create text
- Fonts and typography
- Format type
- Import and export text
- Format paragraphs
- Special characters
- Create type on a path
- Character and paragraph styles
- Tabs
- Text and type
- Find missing fonts (Typekit workflow)
- Update text from Illustrator 10
- Arabic and Hebrew type
- Fonts | FAQ and troubleshooting tips
- Create 3D text effect
- Creative typography designs
- Scale and rotate type
- Line and character spacing
- Hyphenation and line breaks
- Text enhancements
- Spelling and language dictionaries
- Format Asian characters
- Composers for Asian scripts
- Create text designs with blend objects
- Create a text poster using Image Trace
- Create special effects
- Work with effects
- Graphic styles
- Create a drop shadow
- Appearance attributes
- Create sketches and mosaics
- Drop shadows, glows, and feathering
- Summary of effects
- Web graphics
- Best practices for creating web graphics
- Graphs
- SVG
- Create animations
- Slices and image maps
- Drawing
- Import, export, and save
- Import
- Import artwork files
- Import bitmap images
- Import artwork from Photoshop
- Place multiple files | Illustrator CC
- Unembed images
- Import Adobe PDF files
- Import EPS, DCS, and AutoCAD files
- Links information
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Illustrator
- Creative Cloud Libraries in Illustrator
- Save
- Save artwork
- Export
- Export artwork
- Collect assets and export in batches
- Package files
- Create Adobe PDF files
- Extract CSS | Illustrator CC
- Adobe PDF options
- File information and metadata
- Import
- Printing
- Prepare for printing
- Set up documents for printing
- Change the page size and orientation
- Specify crop marks for trimming or aligning
- Get started with large canvas
- Printing
- Overprint
- Print with color management
- PostScript printing
- Print presets
- Printer's marks and bleeds
- Print and save transparent artwork
- Trapping
- Print color separations
- Print gradients, meshes, and color blends
- White Overprint
- Prepare for printing
- Automate tasks
- Data merge using the Variables panel
- Automation with scripts
- Automation with actions
- Troubleshooting
- Crash on launch issues
- Recover files after crash
- File issues
- GPU device driver issues
- Wacom device issues
- DLL file issues
- Memory issues
- Preferences file issues
- Font issues
- Printer issues
- Share crash report with Adobe
Learn about creating and working with type in Adobe Illustrator...
Enter text at a point
Point type is a horizontal or vertical line of text that begins where you click and expands as you enter characters. Each line of text is independent—the line expands or shrinks as you edit it, but doesn't wrap to the next line. Entering text this way is useful for adding a few words to your artwork.
-
Select the Type tool
 or the Vertical Type tool
or the Vertical Type tool .
.The pointer changes to an I-beam within a dotted box. The small horizontal line near the bottom of the I-beam marks the position of the baseline, on which the text rests.
-
(Optional) Set text-formatting options in the Control panel, Character panel, or Paragraph panel.
-
Click where you want the line of text to begin.
Be sure not to click an existing object, because doing so converts the type object into area type or type on a path. If an existing object is located where you want to enter text, lock or hide the object.
-
Enter the text. Press Enter or Return to begin a new line of text within the same type object.
-
When you finish entering text, click the Selection tool
 to select the type object. Alternatively, Ctrl‑click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) the text.
to select the type object. Alternatively, Ctrl‑click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) the text.
For more information about working with type in Illustrator, see this video.
Enter text in an area
Area type (also called paragraph type) uses the boundaries of an object to control the flow of characters, either horizontally or vertically. When the text reaches a boundary, it automatically wraps to fit inside the defined area. Entering text this way is useful when you want to create one or more paragraphs, such as for a brochure.
-
Define the bounding area:

Creating a type area by dragging (top) compared to converting an existing shape to a type area (bottom) If the object is an open path, you must use the Area Type tool to define the bounding area. Illustrator draws an imaginary line between the endpoints of the path to define the boundaries.
-
(Optional) Set text-formatting options in the Control panel, Character panel, or Paragraph panel.
-
Enter the text. Press Enter or Return to begin a new paragraph.
-
When you finish entering text, click the Selection tool
 to select the type object. Alternatively, Ctrl‑click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) the text.
to select the type object. Alternatively, Ctrl‑click (Windows) or Command-click (Mac OS) the text. If you enter more text than can fit within an area, a small box containing a plus symbol (+) appears near the bottom of the bounding area.

Example of overflow text You can resize the text area or extend the path to display the overflow text. You can also thread the text into another object.
For more information about working with type in Illustrator, see this video.
Import text into a path/shape
Place text from a supported file right inside an object, such as a shape. You can place text from files in the .txt or .rtf formats, or files from word-processing applications. For example, you can place text from a .rtf file into a polygonal shape.
-
Create a path/shape using any drawing tool, such as the Rectangle tool, Shaper tool, or the Pen tool. You'll place the text file within this shape.
-
Choose File > Place and select the text file you want to place.
-
After the text file is loaded in the place gun, click the path of the shape.
The text is placed inside the shape. You can now apply the desired styles and effects to it.

Fill type objects with placeholder text
Filling type objects with placeholder text helps you visualize the design better. By default, Illustrator automatically fills new objects created using type tools with placeholder text. The placeholder text retains the font and size applied to the previous type object.
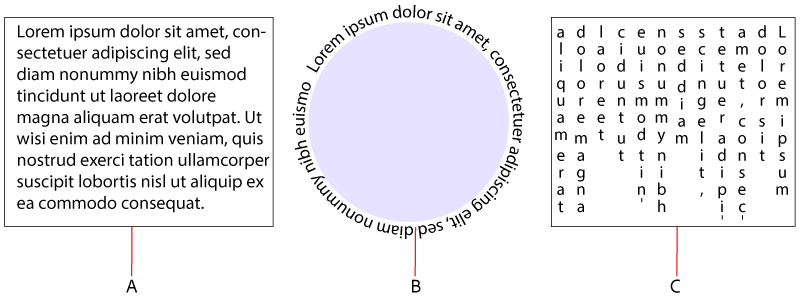
A. Type ToolB. Type On A Path ToolC. Vertical Area Type Tool
Fill only selected type objects with placeholder text
You can disable the default Illustrator behavior of filling all new type objects with placeholder text. Deselect Preferences > Type > Fill New Type Objects With Placeholder Text.

After you disable the default behavior, you can still fill type objects with placeholder text on a case-by-case basis. Follow these steps:
-
Use a Point or Area Type tool to create a type object. Alternatively, select an existing type object on the artboard.
-
Do one of the following:
- Choose Type > Fill With Placeholder Text.
- Right-click the text frame to open the in-context menu. Select Fill With Placeholder Text.
Illustrator fills the type object with placeholder text.
Manage the text area
Resize a text area
You can resize text in different ways, depending on the whether you are creating point type, area type, or text along a path.
There is no limit for the amount of text that can be written using point type, so resizing of the text box is not required in this case.
When using the area type tool, you drag an object and type inside the selected area. In this case, the text resizes when you resize the object using the Direct Selection tool.
When you type text along a path, you can thread text between objects (see Threading text between objects), if the text does not fit in the selected path. In this case also, the text is resized if you resize the path using the Direct Selection tool.
Make sure that the bounding box setting is set to Show Bounding Box. If you are not able to see the bounding box, then click View > Show Bounding Box.
-
To resize, do one of the following:
-
Select the type object using the Selection tool or Layers panel, and drag a handle on the bounding box.

Resizing a text area with the Selection tool -
Select the edge or corner of the type path with the Direct Selection tool
 . Then drag to adjust the shape of the path.
. Then drag to adjust the shape of the path.Tip: Adjusting the type path using the Direct Selection tool is easiest when you're in Outline view.

Resizing a type area with the Direct Selection tool -
Select the type object using the Selection tool or Layers panel, and choose Type > Area Type Options. Enter values for Width and Height, and click OK. If the text area is not a rectangle, these values determine the dimensions of the object's bounding box.
-
Change the margin around a text area
When working with an area type object, you can control the margin between the text and the bounding path. This margin is referred to as the inset spacing.
-
Select an area type object.
-
Choose Type > Area Type Options.
-
Specify a value for Inset Spacing, and click OK.

Type without inset spacing (left) compared to type with inset spacing (right)
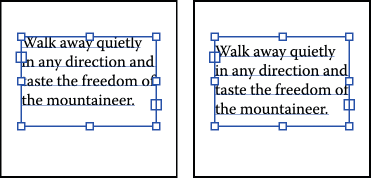
Raise or lower the first baseline in a text area
When working with an area type object, you can control the alignment of the first line of text with the top of the object. This alignment is referred to as the first baseline offset. For example, you can make text stick up above the top of the object or fall a specific distance below the top of the object.
-
Select an area type object.
-
Choose Type > Area Type Options.
-
For First Baseline, choose one of the following options:
Ascent
The height of the "d" character falls below the top of the type object.
Cap Height
The tops of uppercase letters touch the top of the type object.
Leading
Uses the text's leading value as the distance between the baseline of the first line of text and the top of the type object.
x Height
The height of the "x" character falls below the top of the type object.
Em Box Height
The top of the em box in Asian fonts touches the top of the type object. This option is available regardless of the Show Asian Options preference.
Fixed
Specifies the distance between the baseline of the first line of text and the top of the type object in the Min box.
Legacy
Uses the first baseline default used in Adobe Illustrator 10 or earlier.
-
For Min, specify the value for the baseline offset.
Create rows and columns of text
-
Select an area type object.
-
Choose Type > Area Type Options.
-
In the Rows and Columns sections of the dialog box, set the following options:
Number
Specifies the number of rows and columns you want the object to contain.
Span
Specifies the height of individual rows and the width of individual columns.
Fixed
Determines what happens to the span of rows and columns if you resize the type area. When this option is selected, resizing the area can change the number of rows and columns, but not their width. Leave this option deselected if you want row and column widths to change when you resize the type area.

Options for resizing rows and columns Gutter
Specifies the distance between rows or columns.
-
In the Options section of the dialog box, select a Text Flow option to determine how text flows between rows and columns: By Rows
 or By Columns
or By Columns  .
.
Fit a headline across the full width of a type area
-
Select a type tool, and click in the paragraph you want to fit across the type area.
-
Choose Type > Fit Headline.
If you change the formatting of the type, be sure to reapply the Fit Headline command.
Threading text between objects
To thread (or continue) text from one object to the next, you link the objects. Linked type objects can be of any shape; however, the text must be entered in an area or along a path (not at a point).
Each area type object contains an in port and an out port, which enables you to link to other objects and create a linked copy of the type object. An empty port indicates that all the text is visible and that the object isn't linked. An arrow in a port indicates that the object is linked to another object. A red plus sign in an out port indicates that the object contains additional text. This remaining unseen text is called overflow text.
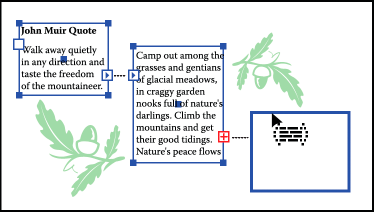
You can break threads and have the text flow into either the first or the next object, or you can remove all threads and have the text stay in place.
When working with threaded text, it can be useful to see the threads. To view threads, choose View > Show Text Threads and then select a linked object.
Thread text
-
Use the Selection tool to select an area type object.
-
Click the in port or the out port of the selected type object. The pointer changes to the loaded text icon
 .
. -
-
To link to an existing object, position the pointer on the object's path. The pointer changes to a
 . Click the path to link the objects.
. Click the path to link the objects. -
To link to a new object, click or drag on an empty part of the artboard. Clicking creates an object of the same size and shape as the original; dragging lets you create a rectangular object of any size.
Another method for threading text between objects is to select an area type object, select the object (or objects) you want to thread to, and then choose Type > Threaded Text > Create.
-
Remove or break threads
-
Select a linked type object.
-
-
To break the thread between two objects, double-click the port on either end of the thread. The text flows into the first object.
-
To release an object from a text thread, choose Type > Threaded Text > Release Selection. The text flows into the next object.
-
To remove all threads, choose Type > Threaded Text > Remove Threading. The text stays in place.
-
Wrap text around an object
You can wrap area text around any object, including type objects, imported images, and objects you draw in Illustrator. If the wrap object is an embedded bitmap image, Illustrator wraps the text around opaque or partially opaque pixels and ignores fully transparent pixels.
Wrapping is determined by the stacking order of objects, which you can view in the Layers panel by clicking the triangle next to the layer name. To wrap text around an object, the wrap object must be in the same layer as the text and located directly above the text in the layer hierarchy. You can drag contents up or down in the Layers panel to change hierarchy.
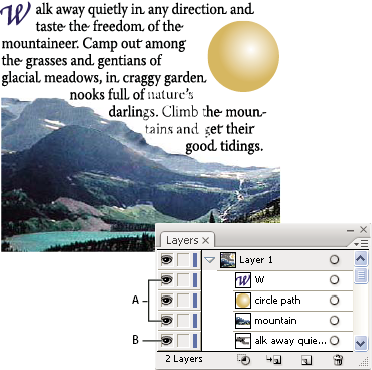
A. Wrap objectsB. Wrapped text
Wrap text
-
Make sure that the following conditions are true for the type you want to wrap:
-
It is area type (typed in a box).
-
It is in the same layer as the wrap object.
-
It is located directly under the wrap object in the layer's hierarchy.
If the layer contains multiple type objects, move any that you don't want to wrap around the wrap object either into another layer or above the wrap object.
-
-
Select the object or objects around which you want the text to wrap.
-
Choose Object > Text Wrap > Make.
Set wrap options
You can set wrap options before or after you wrap the text.
-
Choose Object > Text Wrap > Text Wrap Options and specify the following options:
Offset
Specifies the amount of space between the text and the wrap object. You can enter a positive or negative value.
Invert Wrap
Wraps the text around the reverse side of the object.
Unwrap text from an object
-
Choose Object > Text Wrap > Release.
Align type to object
To align text according to the bounding box of the actual glyphs instead of the font metrics, do the following:
-
Apply the Outline Object live effect to the type object using Effect > Path > Outline Object.
-
Set the Align panel to use preview bounds by selecting the Use Preview Bounds option from the Align panel menu (flyout).
After applying these settings, you get the same alignment as outlined text, while keeping the text live.
Delete empty type objects from your artwork
Deleting unused type objects makes your artwork easier to print and reduces the file size. You can create empty type objects, for example, if you inadvertently click the Type tool in the artwork area and then choose another tool.
-
Choose Object > Path > Clean Up.
-
Select Empty Text Paths, and click OK.
How To Create Text Columns In Illustrator
Source: https://helpx.adobe.com/in/illustrator/using/creating-text.html
Posted by: woodardaffeekly.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How To Create Text Columns In Illustrator"
Post a Comment